The Dictionary Of Photography
A True Historic Record Of The Art & Practice Of Photography 100 Years Ago.
|
Exposure |
||
|
in which F represents the equivalent focus of the objective; D, the distance of the object from the lens, measured along the principal axis; d, the working aperture of the lens - with doublets
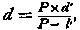 where P is the equivalent focus of the front where P is the equivalent focus of the frontlens, d' the diameter of the diaphragm, / the distance of the centre of the diaphragm from the optical centre of the front lens ; N, the number of degrees of Warnerke's sensitometer which the plate used shows. N, with the most sensitive plates, = 25, and varies usually between 16 and 23.
The co-efficient
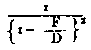 with landscape is about 1, because - with landscape is about 1, because -then D is great; on the other hand, it comes considerably into account in enlargements, since then D is only small. In the above, it must be noticed that the absorption, as well as the reflection of the lenses of the objective, is not calculated. The same has a mean result of loss of light of about 20 per cent.
 Clouds ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 00005
Sea ...... ... ...... ... ... 0001
Snow ... ... ... ... ... ... ... o*ooi
Ships on sea ... ... ... ... ... ... 0.003
Glaciers with rocks .. ... ... ... ... 0003
Open landscape (panorama) ... ... ... ... 0003
Foliage, with water or white houses.. ... ... 0.005
Foliage only, and near ... ... ... ... ... o'Oi
Living subjects, portraits, still life, etc. ...... O'OI
Reproduction of black lines on white ground ... 002
Value of
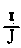 According to Eder, Abney, and Vogel. According to Eder, Abney, and Vogel.Direct upright sunlight; for Paris, June 21st, noon ;
also if the sun stands 66o above the horizon ... 1
Diffused light, bright weather ......... 4
.. .. sky covered............4 to 10
Under trees ...... ............ 270
In the studio ... ... ... ... ... ... 12
In a room, I metre from window ... ... ... 70
Well-lighted church ...... ......... 200
296 |
||